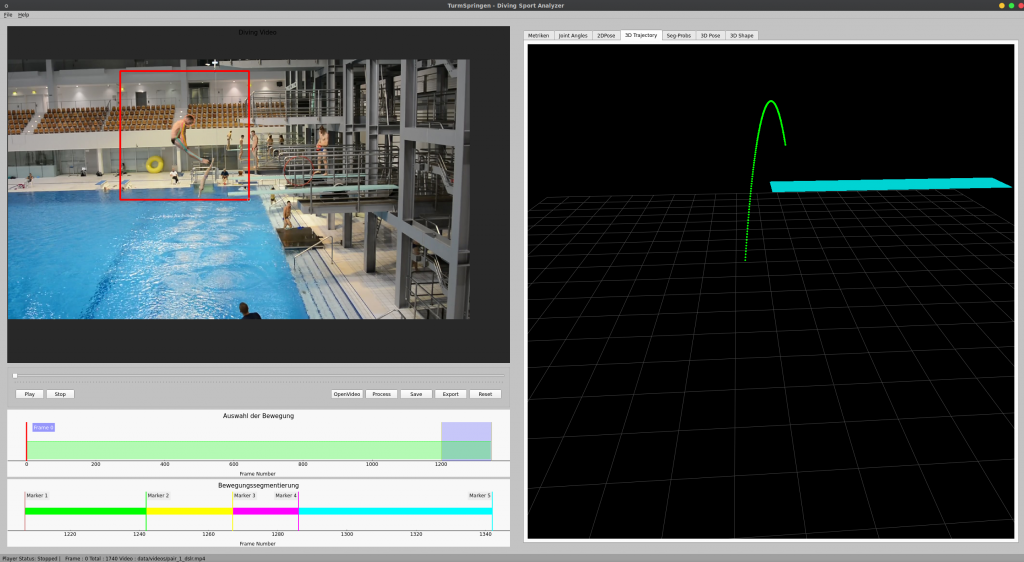
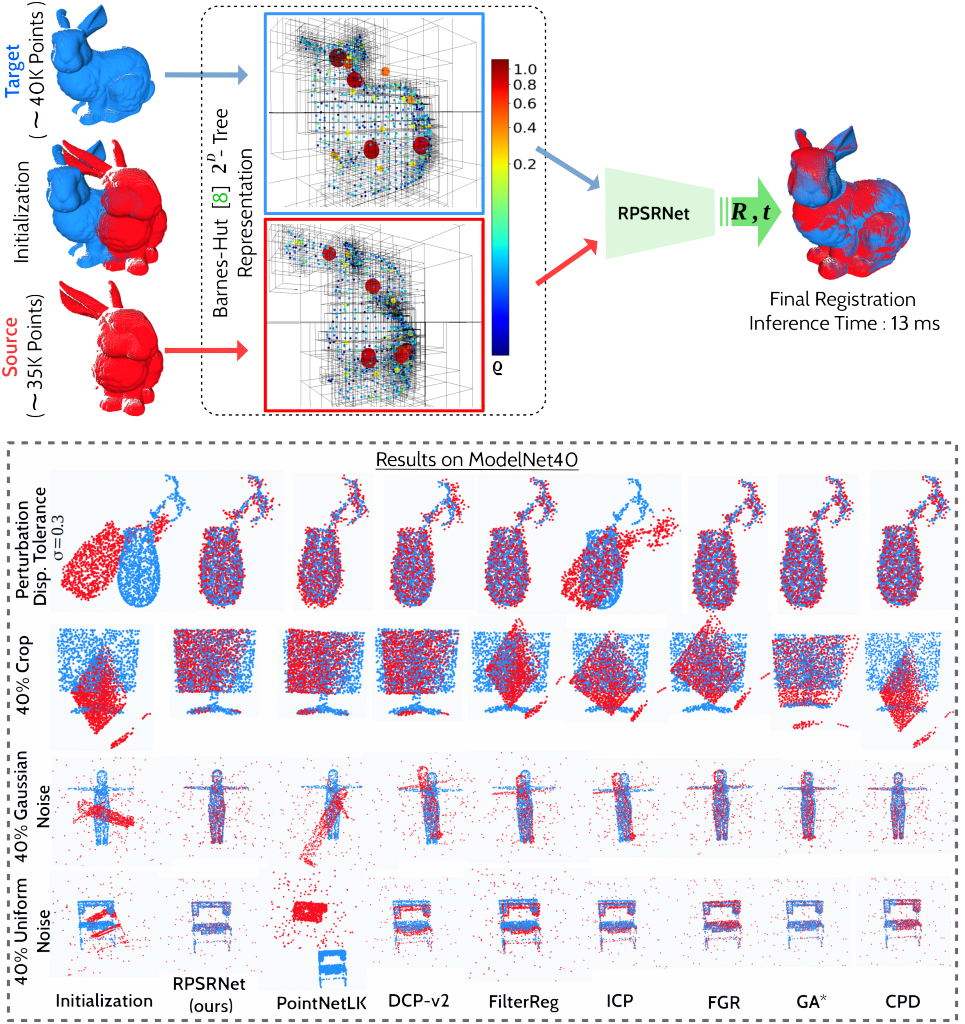
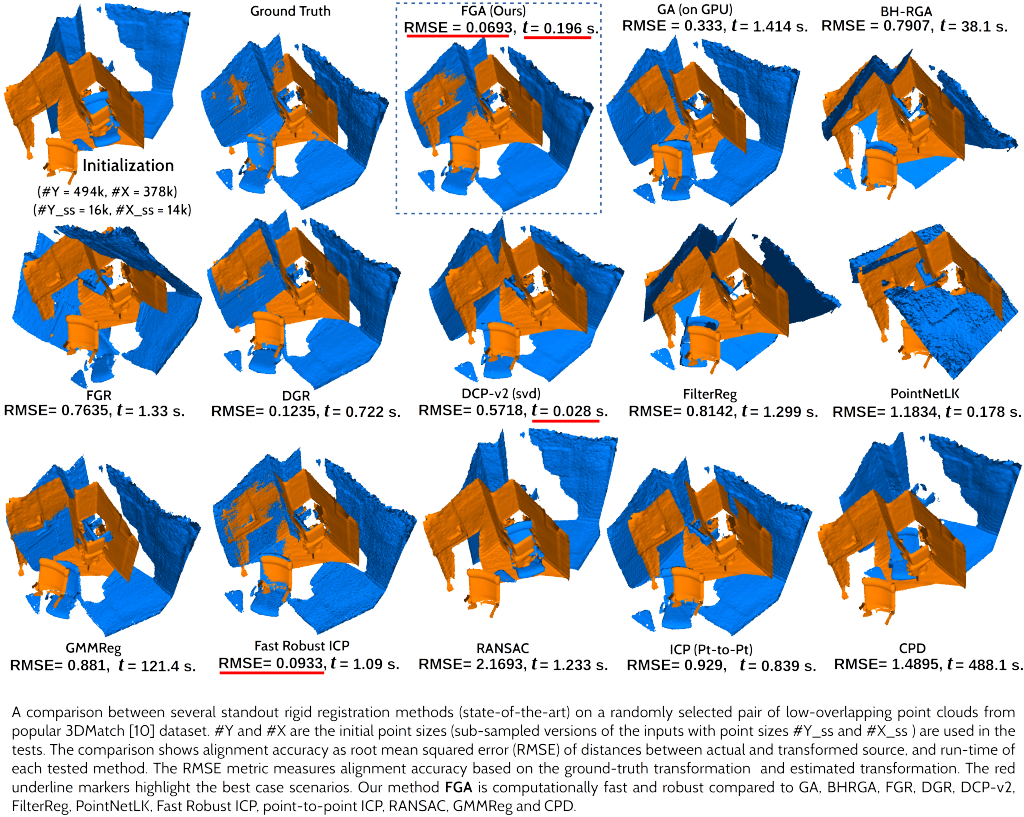
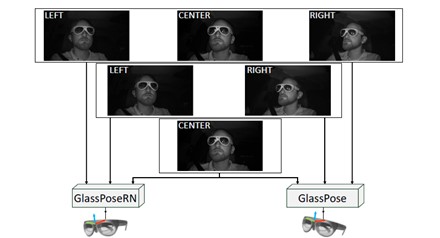
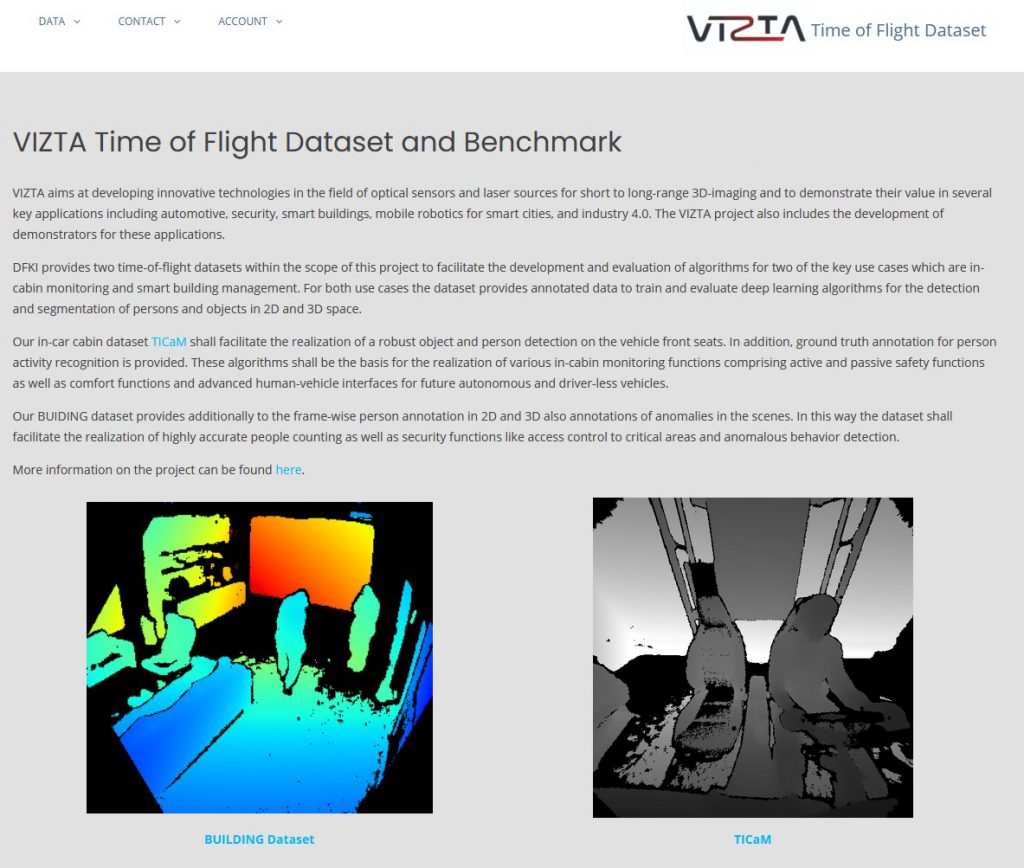
DFKI Augmented Vision is working with Stellantis on the topic of Radar-Camera Fusion for Automotive Object Detection using Deep Learning since 2020. The collaboration has already led to two publications, in ICCV 2021 (International Conference on Computer Vision – ERCVAD Workshop on “Embedded and Real-World Computer Vision in Autonomous Driving”) and WACV 2022 (Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision).
The 2 publications are:
1. Deployment of Deep Neural Networks for Object Detection on Edge AI Devices with Runtime Optimization, Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops – ERCVAD Workshop on Embedded and Real-World Computer Vision in Autonomous Driving
Lukas Stefan Stäcker, Juncong Fei, Philipp Heidenreich, Frank Bonarens, Jason Rambach, Didier Stricker, Christoph Stiller
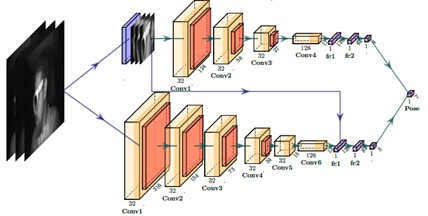
This paper discusses the optimization of neural network based algorithms for object detection based on camera, radar, or lidar data in order to deploy them on an embedded system on a vehicle.
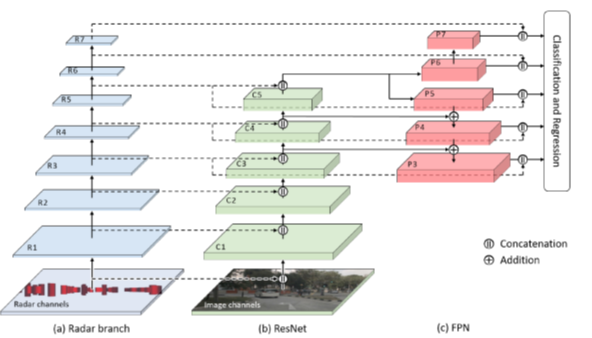
2. Fusion Point Pruning for Optimized 2D Object Detection with Radar-Camera Fusion, Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2022
Lukas Stefan Stäcker, Juncong Fei, Philipp Heidenreich, Frank Bonarens, Jason Rambach, Didier Stricker, Christoph Stiller
This paper introduces fusion point pruning, a new method to optimize the selection of fusion points within the deep learning network architecture for radar-camera fusion.
Please view the abstract here: Fusion Point Pruning for Optimized 2D Object Detection with Radar-Camera Fusion (dfki.de)

Contact: Dr. Jason Rambach